9 Find the derivative of the following function f ( x ) = (ln x ) cos x ;Answer to Find the first derivative of y= ln (x^{5/2} square root{1x^{10}}) By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to`y=ln(tanh(x/2))` The derivative formula of natural logarithm is `d/dxln(u) = 1/u*(du)/dx` Applying this formula, the derivative of the function will be
5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
Partial derivative of ln(x^2+y^2)
Partial derivative of ln(x^2+y^2)-Derivative of ln(xsqrt(1x^2)), Full playlist https//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PLj7p5OoL6vGzLwDjpT3gOA1K3RwUo8jDIf you enjoy my videos, then you canDifferentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 2 n = 2 Since y 2 y 2 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of y 2 y 2 with respect to x x is 0 0 Combine fractions Tap for more steps Add 2 x 2 x and 0 0 Combine 2 2 and 1 x 2 y 2 1 x 2 y 2



The Derivative Of Ln X Intuition Proof And Examples
4618 views around the world You can reuse this answer Creative Commons LicenseAt the point (1, 0) y '(1) = By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystepPlease Subscribe here, thank you!!!
Calculus Find the Derivative d/dx y = natural log of e^ (x^2) y = ln (ex2) y = ln ( e x 2) Use logarithm rules to move x2 x 2 out of the exponent d dx x2ln(e) d d x x 2 ln ( e) The natural logarithm of e e is 1 1 d dx x2 ⋅1 d d x x 2 ⋅ 1 Multiply x2 x 2 by 1 1 d dx x2 d d x x 2Derivative of 5*(ln(x))^2 Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processThis video illustrates the tangent line to the 3D surface to illustrate the meaning of the value of a directional derivativewebsite http//mathispower4ucom
You can see that along the line y = x that will simplify to y ′ = 1 as it should Note that the point ( 4, 2) is a solution to the original equation The derivative there is y ′ = 1 / 2 − log 2 2 − log 4 which is about − 0314 which looks about right based on the graph above Let `f(x)= lnx/x^2` `` We will use the quotient rule to find the derivative We know that if `f(x)= u/v, ==gt f'(x)= (u'vuv')/v^2` `` ==> `f(x)= lnx/x^2`In mathematics, a function (or map) f from a set X to a set Y is a rule which assigns to each element x of X a unique element y of Y, the value of f at x, such that the following conditions are met 1) For every x in X there is exactly one y in Y, the value of f at x;
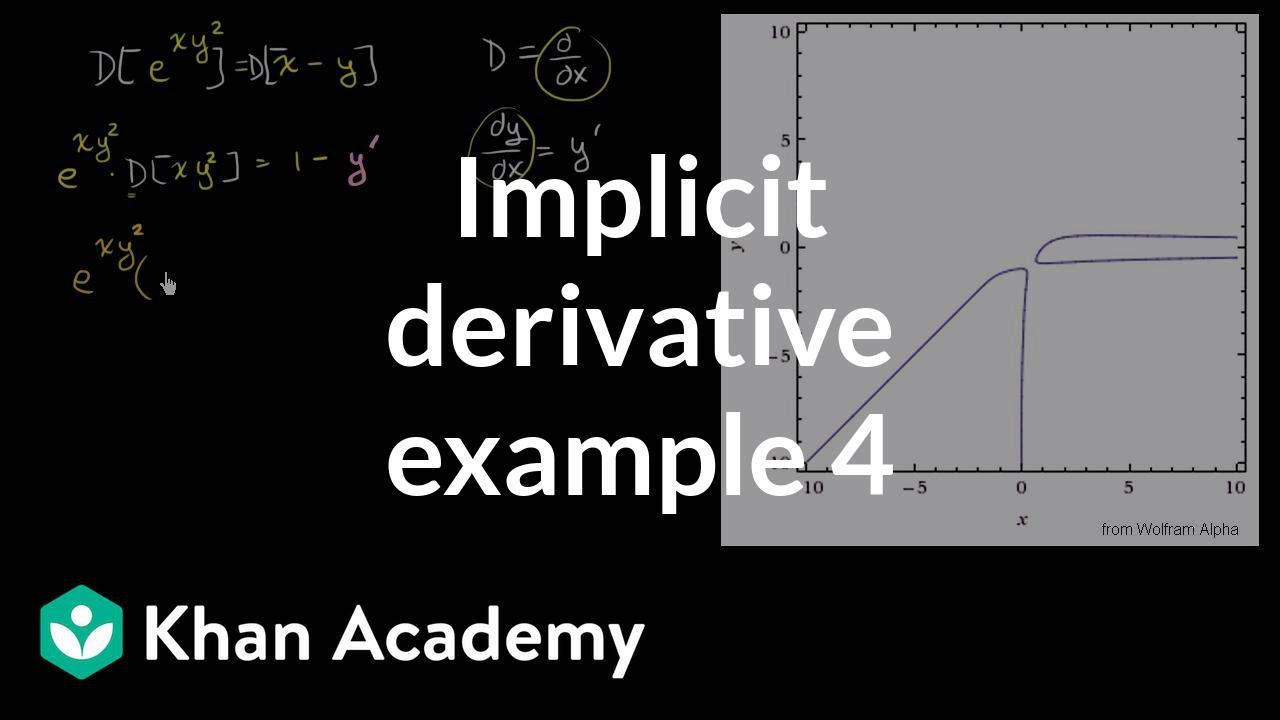



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More
Thus, the derivative of ln x2 is 2/x Note this result agrees with the plots of tangent lines for both positive and negative x For x = 2, the derivative is 2/2 = 1, which agrees with the plot And for x = 2, the derivative is 2/(2) = 1, which agrees with the negative sloping tangent line at x = 2Derivative of Ln(x2) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processDerivative of 2x*ln(x)2e^(2x) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process




Let Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Determine The Derivative Y At Chegg Com



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic
Question Find the derivative of z = x ln y at the point (1, 2) in the direction making an angle of 30 with the positive xaxis This question hasn't been solved yet Ask an expert Ask an expert Ask an expert done loading Find the derivative of z = x ln y at the point (1, 2) in the direction making an angle of 30 with the positive xaxisImplicit\derivative\\frac {dy} {dx},\ (xy)^2=xy1 \frac {\partial} {\partial y\partial x} (\sin (x^2y^2)) \frac {\partial } {\partial x} (\sin (x^2y^2)) derivativecalculator \frac {d} {dx}\left (ln\left (x^ {2}\right)\right) en Sign In Sign in with Office365 Sign in with Facebook So I feel we would get$$\frac{\partial}{\partial x} \ln(x^2y^2)=\frac{2x}{x^2y^2}$$ and with respect to $y$ $$\frac{\partial}{\partial y} \ln(x^2y^2)=\frac{2y}{x^2y^2}$$ Is that right?




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 Fx



Search Q Product Rule Tbm Isch
Derivative of 2x (x^2)* (e^y) Derivative of 2x (x^2)* (e^y) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand theLet {eq}y=x^x {/eq} Compute the derivative {eq}y'(\frac{1}{2}) {/eq} a {eq}1\ln 2 {/eq} b {eq}\frac{1}{\sqrt 2} {/eq} c {eq}\frac{1}{4} {/eq}Derivatives › Second Derivative Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Mean, Median & Mode Scientific Notation Arithmetics Algebra




Let Y Ln X2 Y2 Determine The Derivative Y At Chegg Com



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Differentiation Ii Exam Questions Pdf
In doing this, the Derivative Calculator has to respect the order of operations A specialty in mathematical expressions is that the multiplication sign can be left out sometimes, for example we write "5x" instead of "5*x" The Derivative Calculator has to detect these cases and insert the multiplication signDerivative of (2x)ln(x)^2 Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processOkay, take the derivative of the first function before the product, then derivative of E to the X is just e to the x times leave natural Lagerback's alone, the other function to the right Then you leave the first function alone, which is just e to the X, And then you take the drift of of the second piece right here, and the drift of of natural



What Is The Differentiation Of Ln Sinx Quora




Lesson 16 Derivatives Of Logarithmic And Exponential Functions
//googl/JQ8NysFirst Order Partial Derivatives of f(x, y) = ln(x^4 y^4)Firstly log (ln x) has to be converted to the natural logarithm by the change of base formula as all formulas in calculus only work with logs with the base e and not 10 Hence log ( ln x ) = ln ( ln x ) / ln (10) and then differentiating this gives 1/ln (10) * d (ln (ln x)) / dxDeriving them gives f ′ (x) = 1 / x and g ′ (x) = 4x Insert this into the chain rule and you get h ′ (x) = 1 2x2 ⋅ 4x = 2 x You did just fine, and you correctly applied the chain rule You correctly found the derivative All you may want to do now is to simplify (ln(2x2)) ′ = 2x x2 = 2x x ⋅ x = 2 x
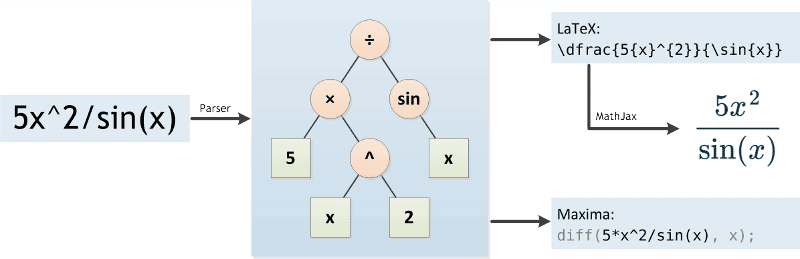



Derivative Calculator With Steps




Partial Derivative Of Fx Y Ln X2 Y2 Gauthmath
Find the Derivative d/dx y = natural log of (x^21)^3 Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set as The derivative of with respect to is Replace all occurrences of with Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where andWorked problem in calculus The derivative of f(x) = ln(ln(x^2 1)) is calculated using the chain rule twiceAnswer to Let y = ln (x^2 y^2) Determine the derivative y '




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps




Find Derivative Of Y E Sqrt Sin Ln X 2 7 5
Derivative of ln(x), with definition & implicit differentiation, proof of derivative of ln(x), derivative of ln(x) with definition of derivative, derivative3) If x and y are in X, then f(x) = fQuestion Find The Derivative Of The Function Y = X^2 Ln X^2 2(x Ln X) 2x^2(1 Ln X^2)/x^2 2x(1 Ln X^2) 2x Ln X^2 This problem has been solved!



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Proof The Derivative Of Ln X Is 1 X Video Khan Academy
Then $\ln{y} = x^2 \ln{x}$; Use the Chain Rule dy dx = 2(lnx)( 1 x) dy dx = 2lnx x Answer linkX > 1 Solution Applying logarithmic function to both sides of the given equations ln y = ln ( (ln x ) cos x ) = (cos x ) ln (ln x ) Di/erentiating with respect to x implicitly, 1 y y 0 = ( ° sin x ) ln (ln x ) (cos x ) ± 1 ln x ± ( 1 x ) = ( ° sin x ) ln (ln x
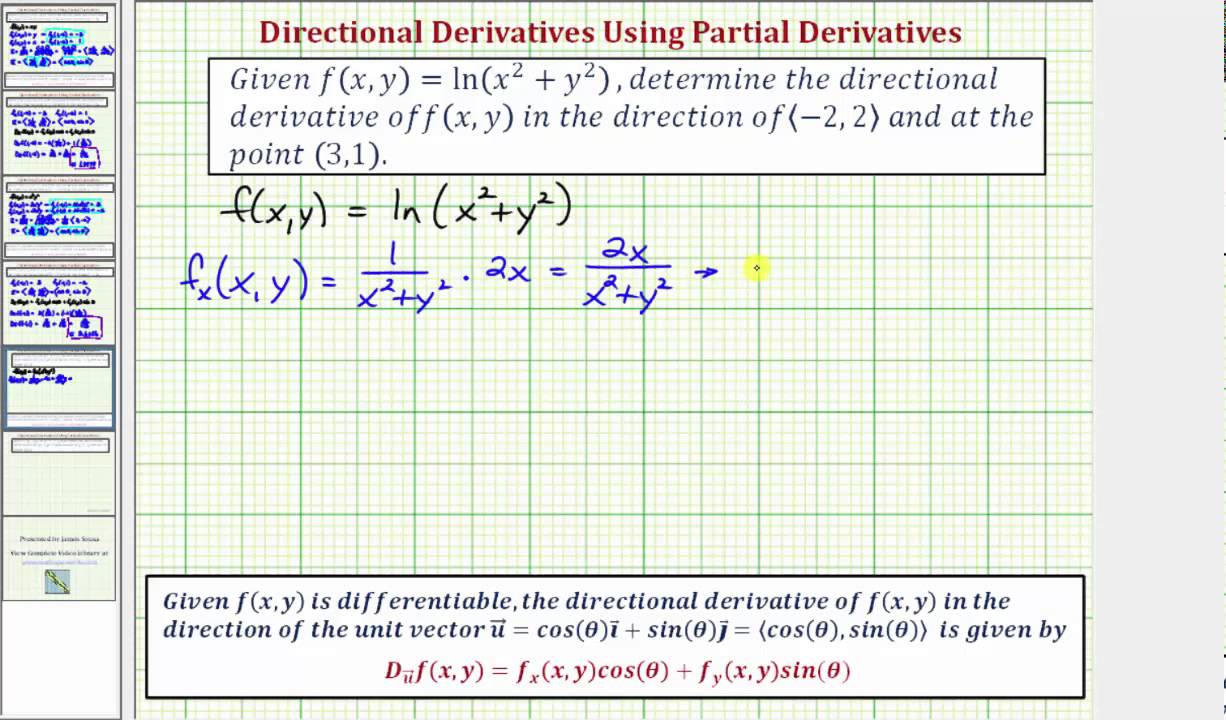



Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube
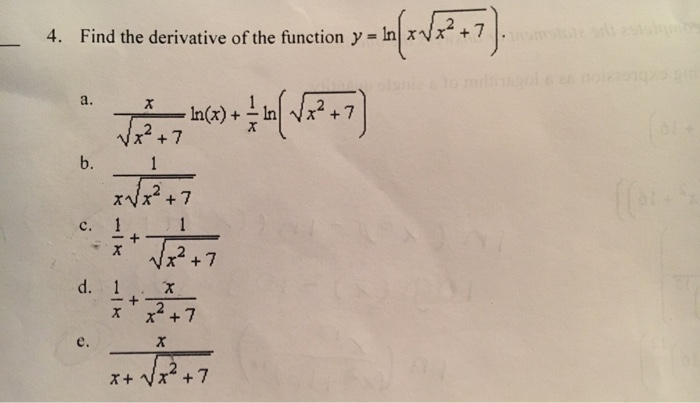



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Ln X Chegg Com
The power property of logs states that ln(x y) = yln(x) In other words taking the log of x to a power is the same as multiplying the log of x by that power We can therefore use the power rule of logs to rewrite ln(x 2) as f(x) = ln(x 2) = 2ln(x) How to find the derivative of ln(x 2) using the power rule of logs $$ \frac{d}{dx} \ln(x \sqrt{ x^{2} y^{2} }) $$ What I've done so far $$1\frac{05(x^{2})^{05}2x}{x\sqrt{x^{2}y^{2}}}$$ $$1\frac{\frac{x}{(x^{2})^{05 The derivative of ln(x) with respect to x is (1/x) The derivative of ln(s) with respect to s is (1/s) In a similar way, the derivative of ln(2x 2) with respect to 2x 2 is (1/2x 2) We will use this fact as part of the chain rule to find the derivative of ln(2x 2) with respect to x How to find the derivative of ln(2x 2) using the Chain Rule




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
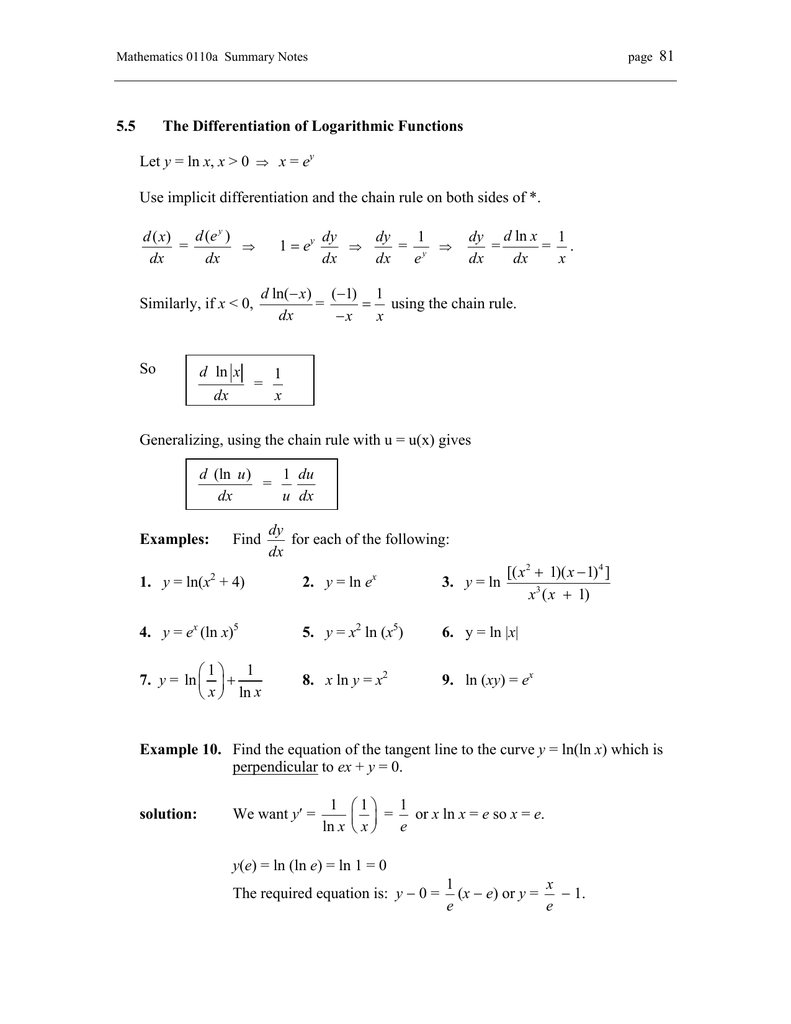



5 5 The Differentiation Of Logarithmic Functions Let Y Ln X X 0
How to find the derivative of the ln(x)Please visit the following website for an organized layout of all my calculus videoshttp//wwwsvhssimik12caus/cmDerivative of ln(x^2) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processTaking a derivative on both sides and using the chain rule for the left leads to $$\frac{y'}{y} = 2x \ln{x} \frac{x^2}{x}$$ Share Cite Follow answered Oct 18 '13 at 501 user user $\endgroup$ 2 1 $\begingroup$ Implicit differentiation should be taught alongside the chain rule
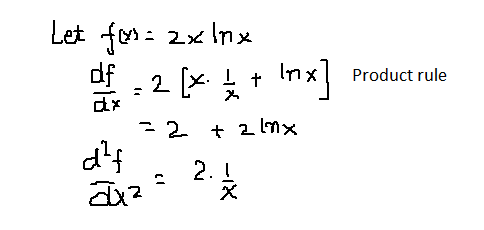



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of 2x Ln X Socratic




Derivative Calculator Wolfram Alpha
y = ln x 2 = 2 ln x The derivative will be simply 2 times the derivative of ln x So the answer is `d/(dx)ln\ x^2=2 d/(dx)ln\ x=2/x` We can see from the graph of y = ln x 2 (curve in black, tangent in red) that the slope is twice the slope of y = ln x (curve in blue, tangent in pink)2) If x and y are in X, then f(x) = y;Example find the derivative of f(x) = ln(1 x)(1 x 2) 2 (1 x 3) 3 Solution The last thing that we want to do is to use the product rule and chain rule multiple times
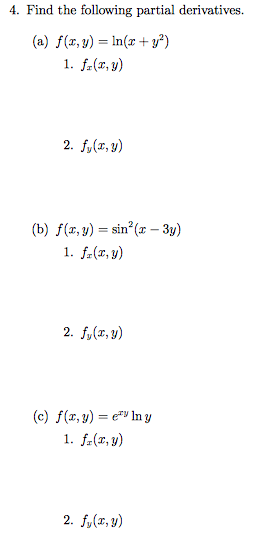



4 Find The Following Partial Derivatives A Chegg Com




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series {\partial x}(\ln(x^{2}y^{4})z) en Related Symbolab blog posts Practice Makes Perfect Learning math takes practice, lots of practice Just like running, it takesUseful resource https//amznto/2RvJIyVImage Page http//calculuscoachescom/indexphp/home/derivativeoflnx2/Derivative of 2ln(x)^y Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic




Solving The Derivative Of Ln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Derivative of (x^2ln(3*x)) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process




First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Youtube
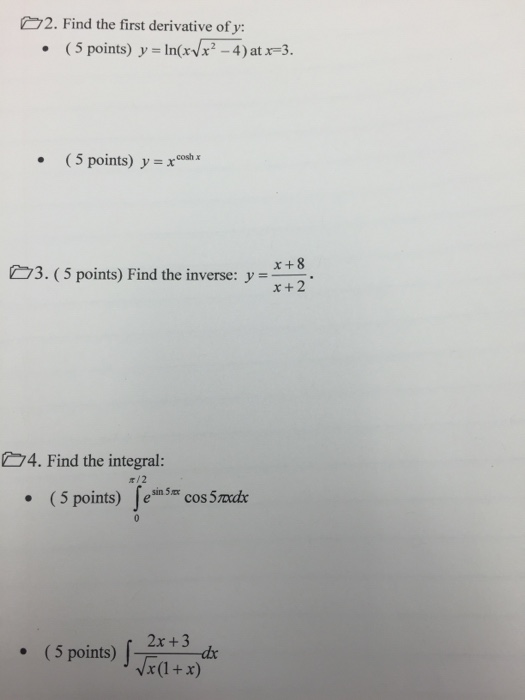



Find The First Derivative Of Y Y Ln X Squareroot Chegg Com




Find The Derivative Y Ln X X 6 Y E X 5 Lnx Chegg Com
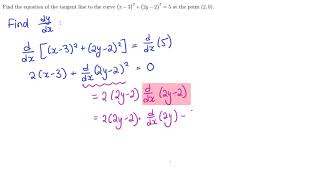



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation
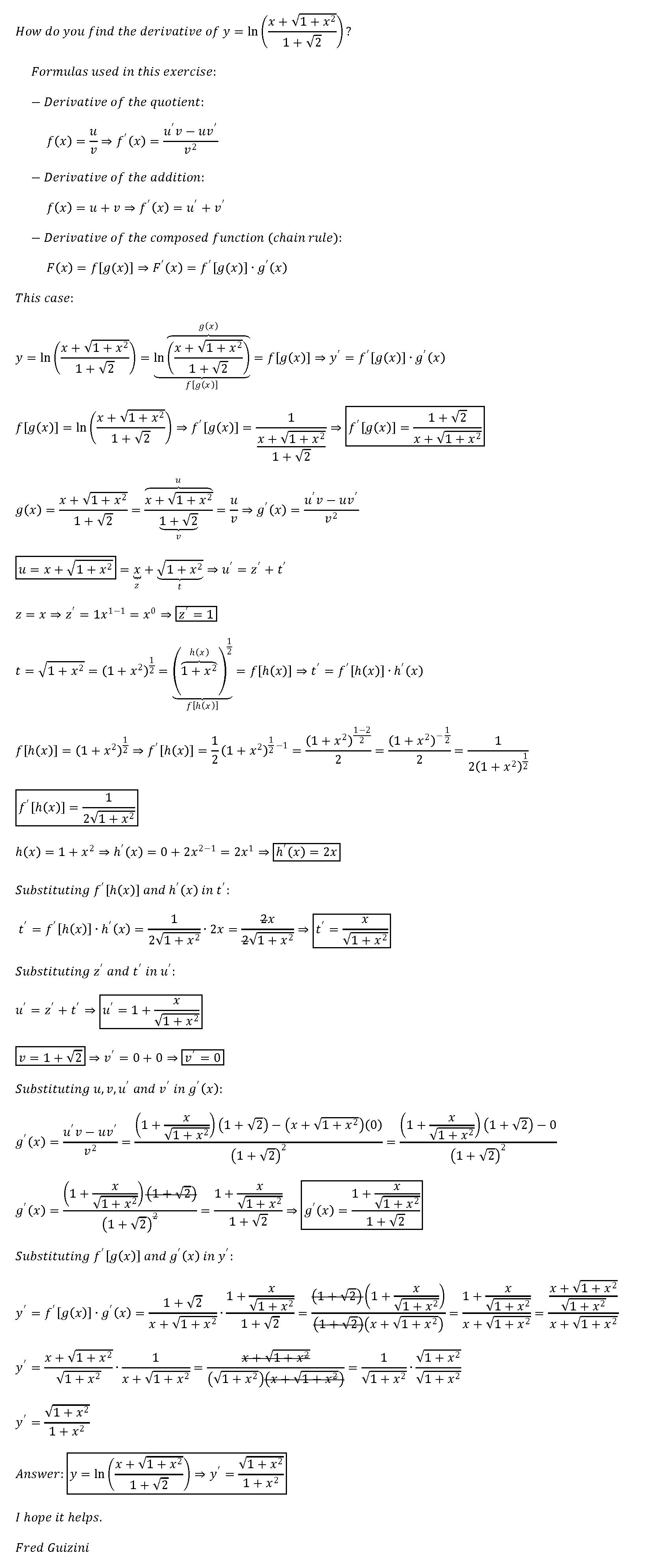



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y Ln X Sqrt 1 X 2 1 Sqrt2 Socratic




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
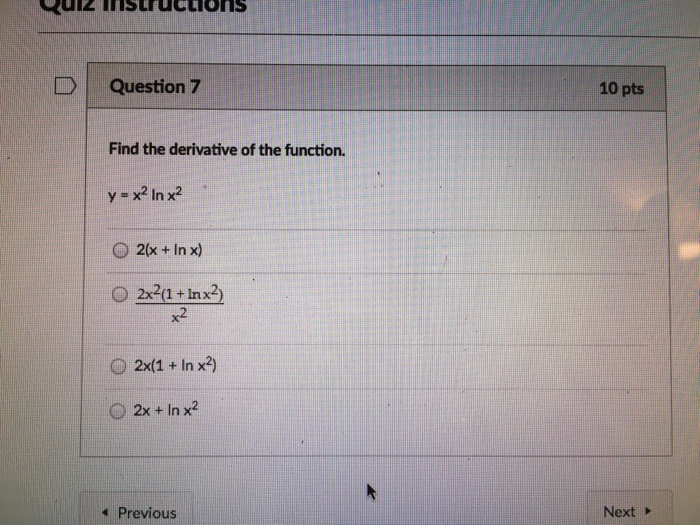



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y X 2 Ln X 2 Chegg Com




How To Differentiate 2 2x Quora
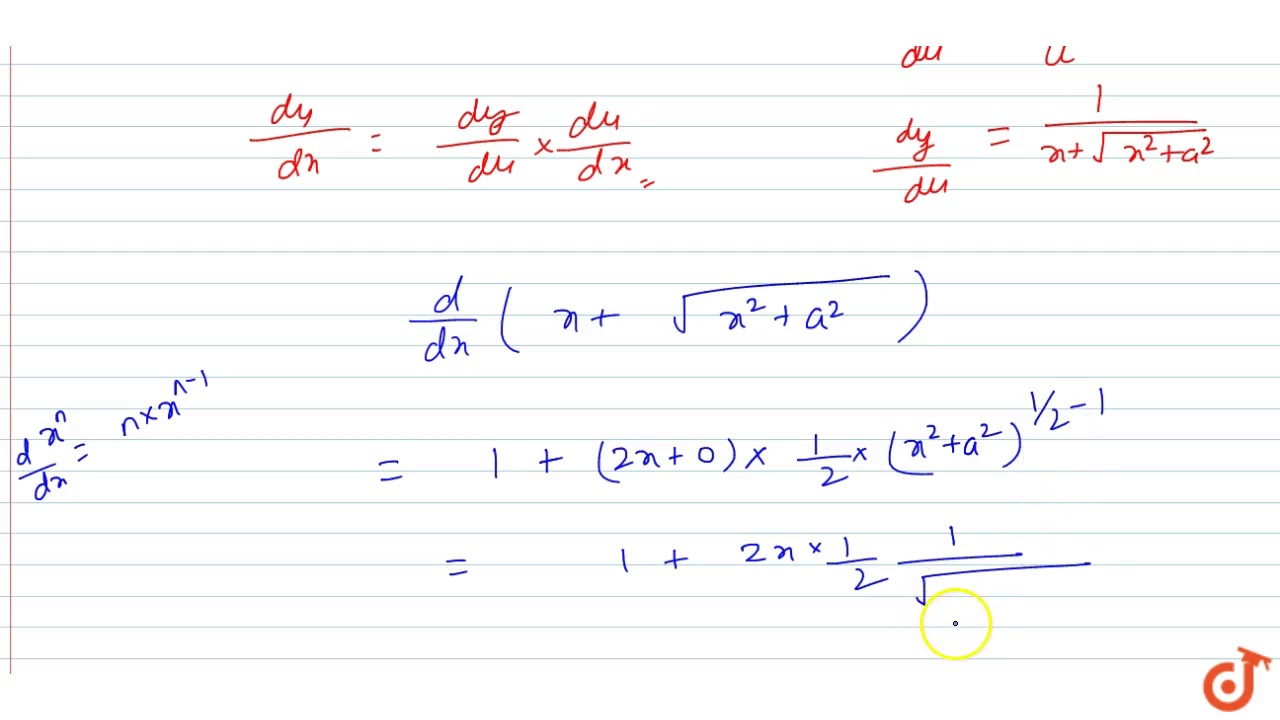



Y Ln X Sqrt X 2 A 2 Find Dy Dx Youtube




What S More Solve For The Derivatives Of The Fol Gauthmath



The Derivative Of Ln X Intuition Proof And Examples




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More
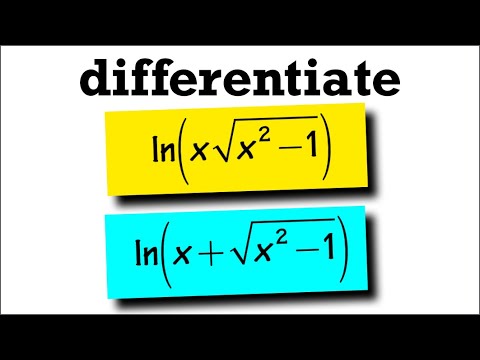



Derivative Of Ln X Sqrt X 2 1 Vs Derivative Of Ln X Sqrt X 2 1 Youtube
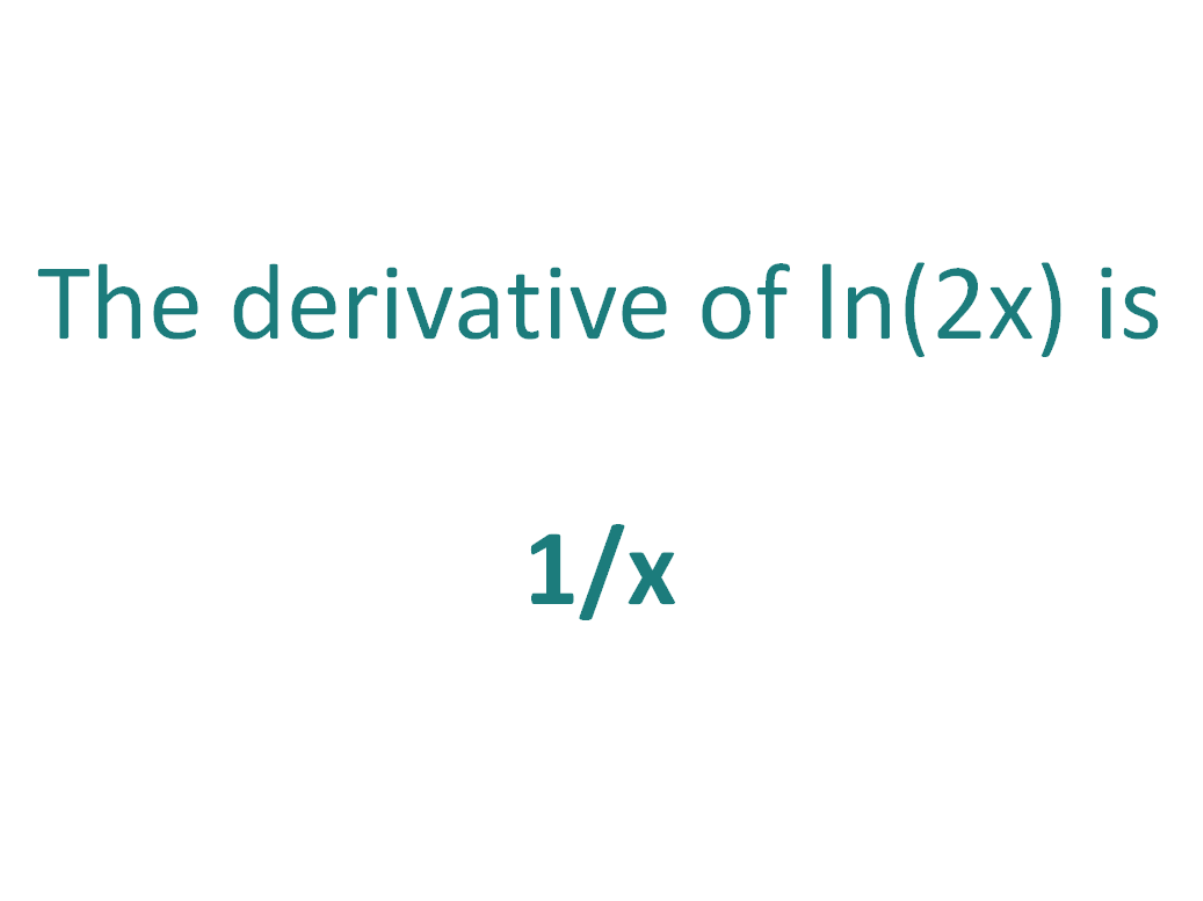



The Derivative Of Ln 2x Derivativeit
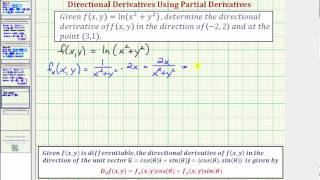



Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube




Learning Task 1 Determine The Derivative Of The F Gauthmath
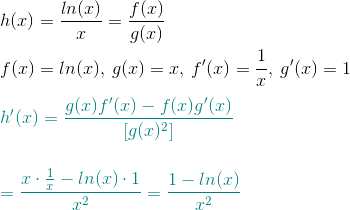



Finding The Derivative Of Ln X X How To Steps Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
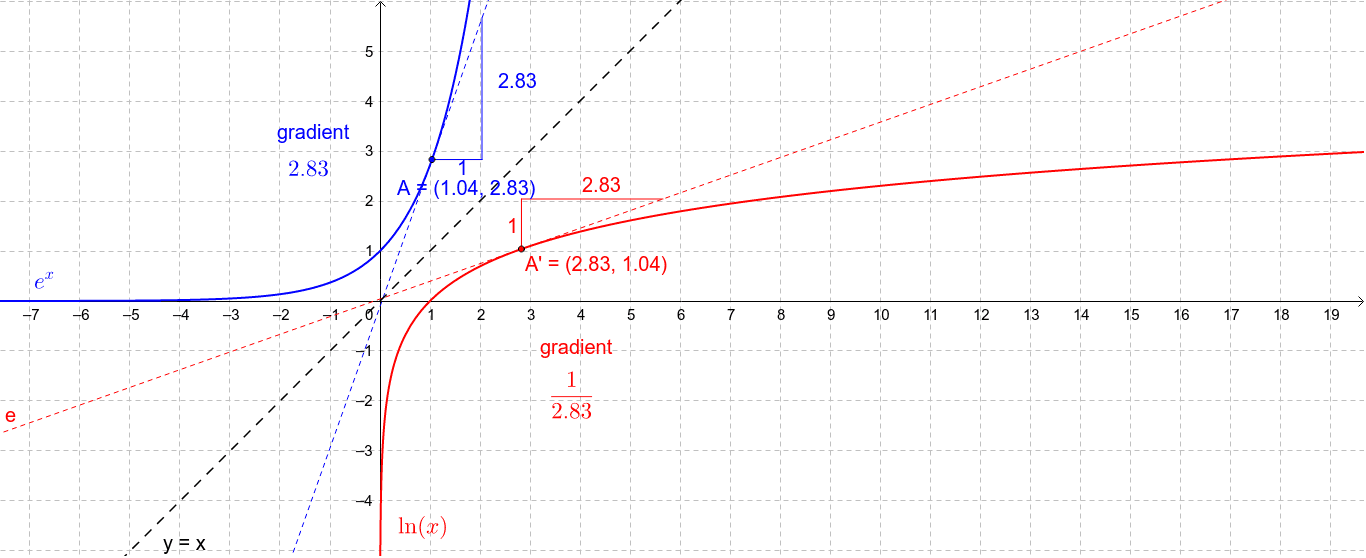



Derivative Of Natural Log Y Ln X Geogebra




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
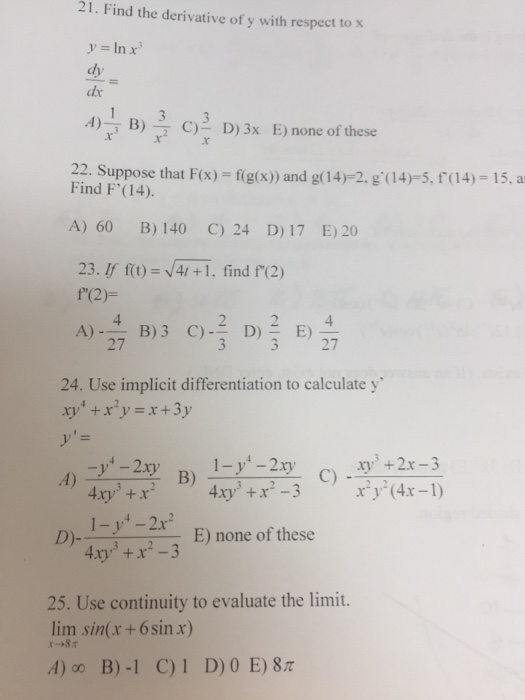



Find The Derivative Of Y With Respect To X Y Ln Chegg Com




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Find The Derivative Of The Function F X Ln X 3 Chegg Com




Help Please For 1 2 6 Find The First Order Partial Chegg Com




How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Ln X X 2 1 1 2 Socratic
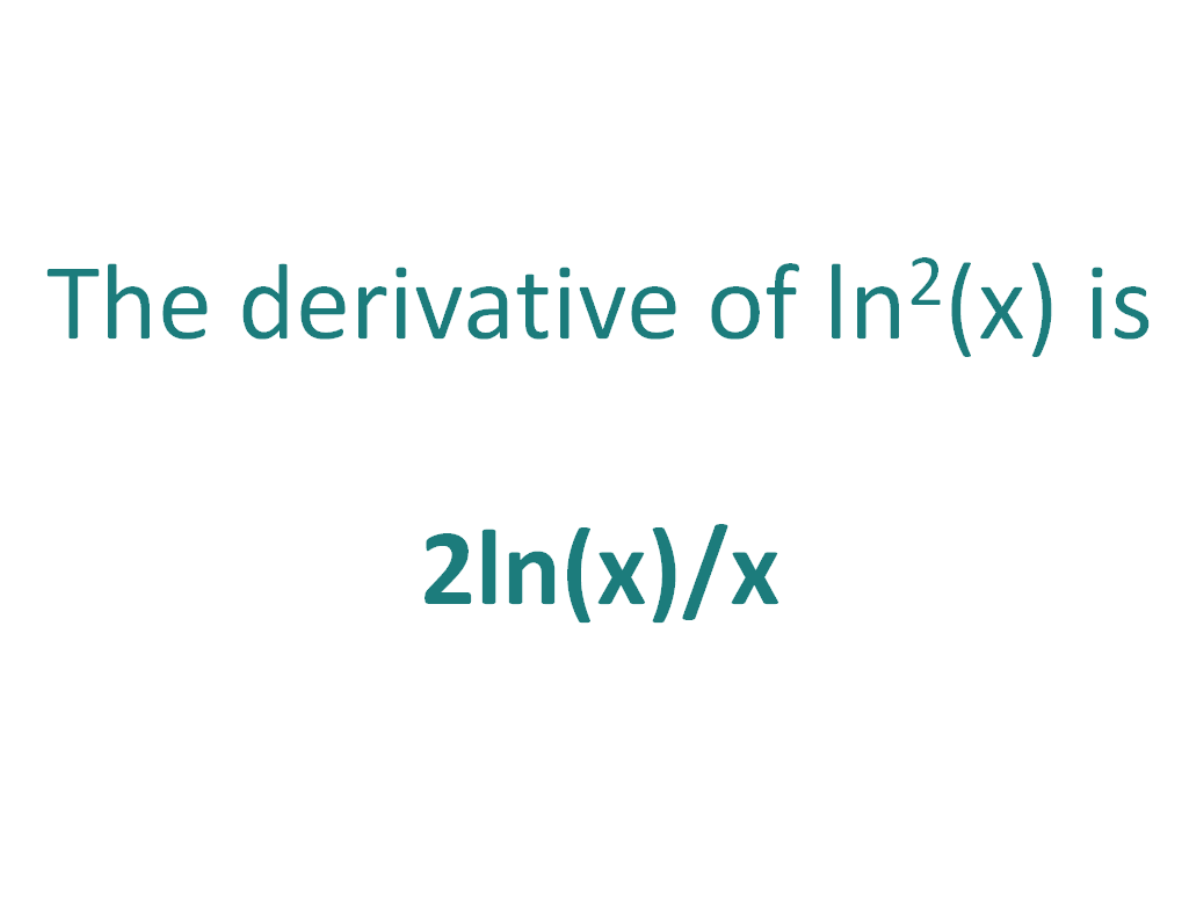



The Derivative Of Ln 2 X Derivativeit




Partial Derivative Of Fx Y Ln X2 Y2 Gauthmath




Logarithmic Derivatives Y Ln X 8 1 3 2 Youtube




Solving The Derivative Of Ln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
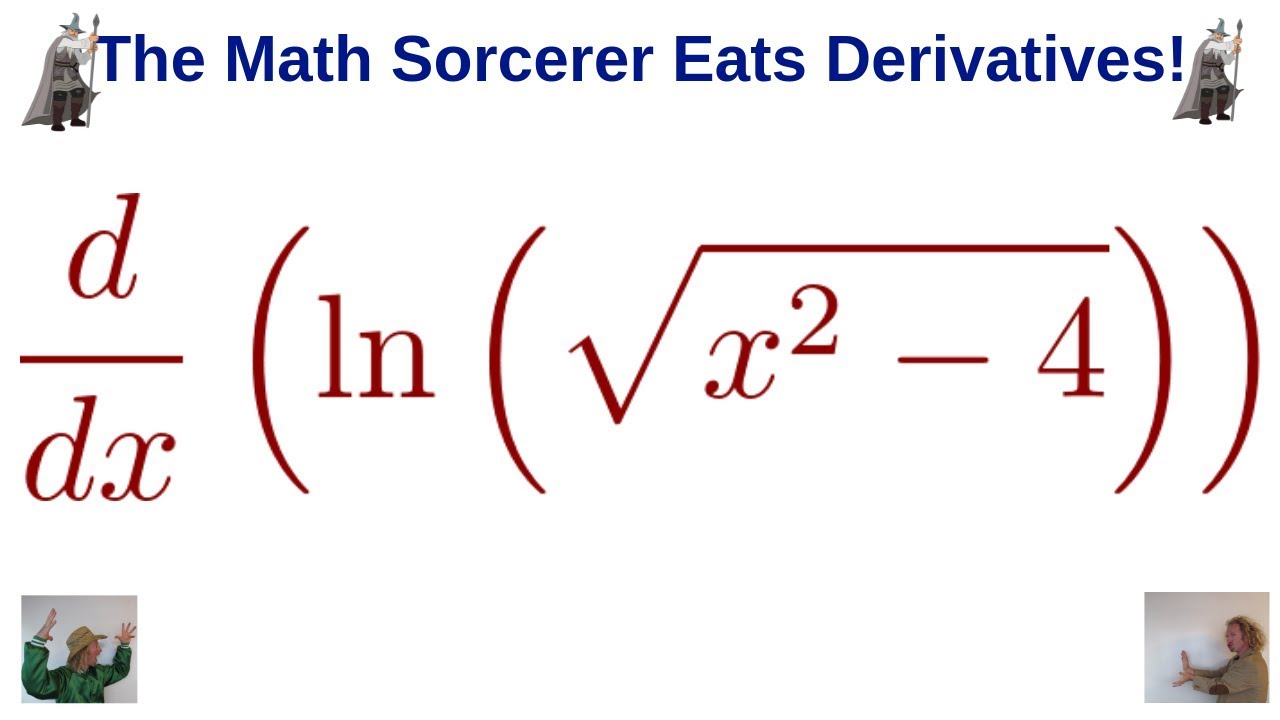



Larson Calculus 5 1 50 Differentiate Ln Sqrt X 2 4 Youtube



3




Derivative Of Ln X Lnx 2 1 Lnx More




F X Ln Ax B Find The Derivative
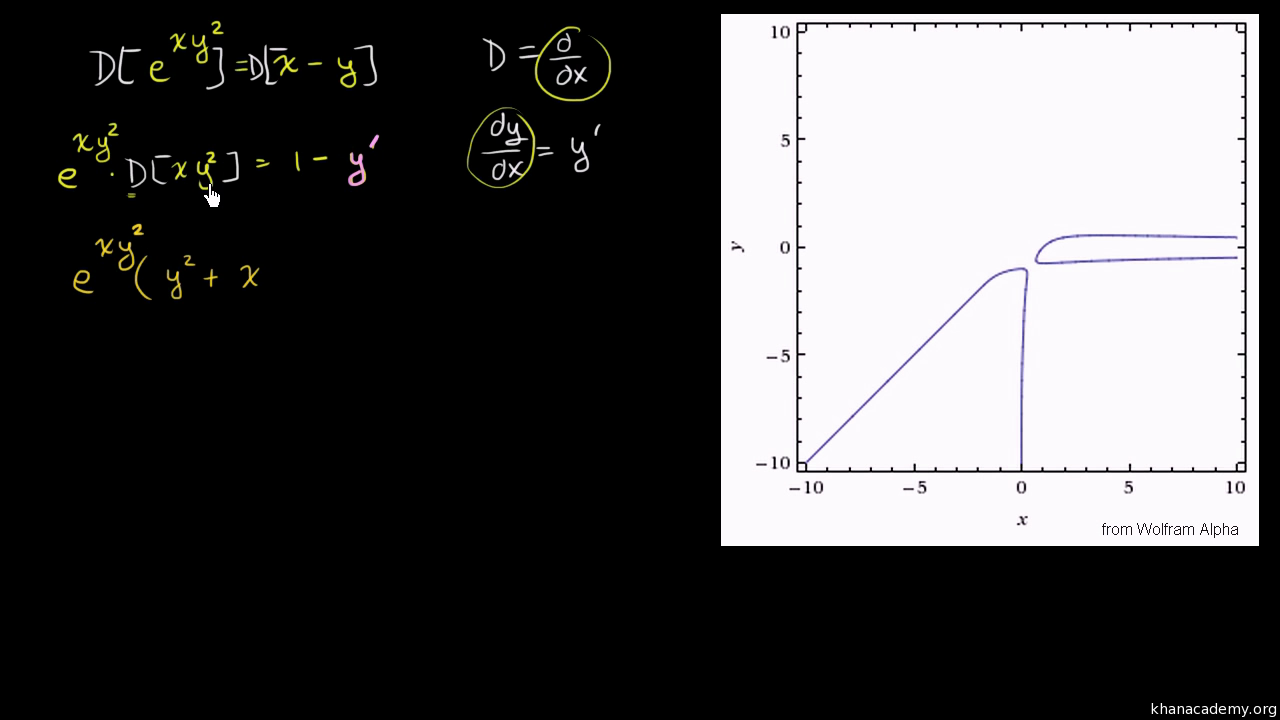



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
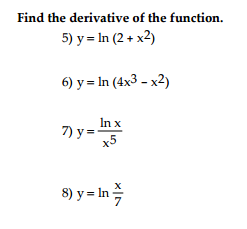



Find The Derivative Of The Function 5 Y Ln 2 Chegg Com



Q Tbn And9gcq9arl5ab K Kkztqdma6czzlslnfprp6ljv7o6a18 5qqda4yy Usqp Cau




Derivative Of Ln X Video Khan Academy




Find The First Derivative Of Y 2 Ln X2 E1 3 A Gauthmath
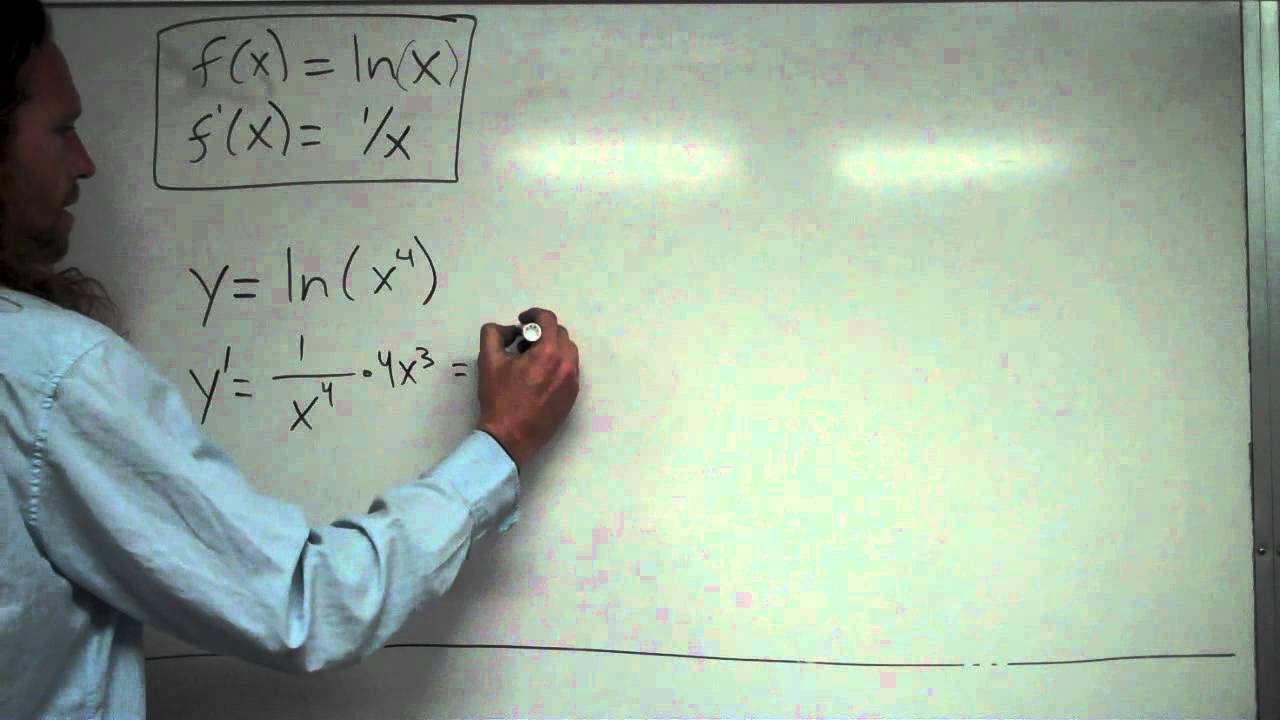



Derivative Of Ln X Youtube
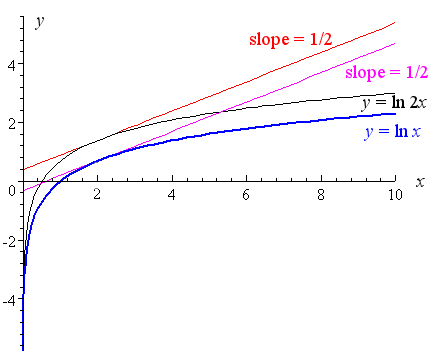



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download
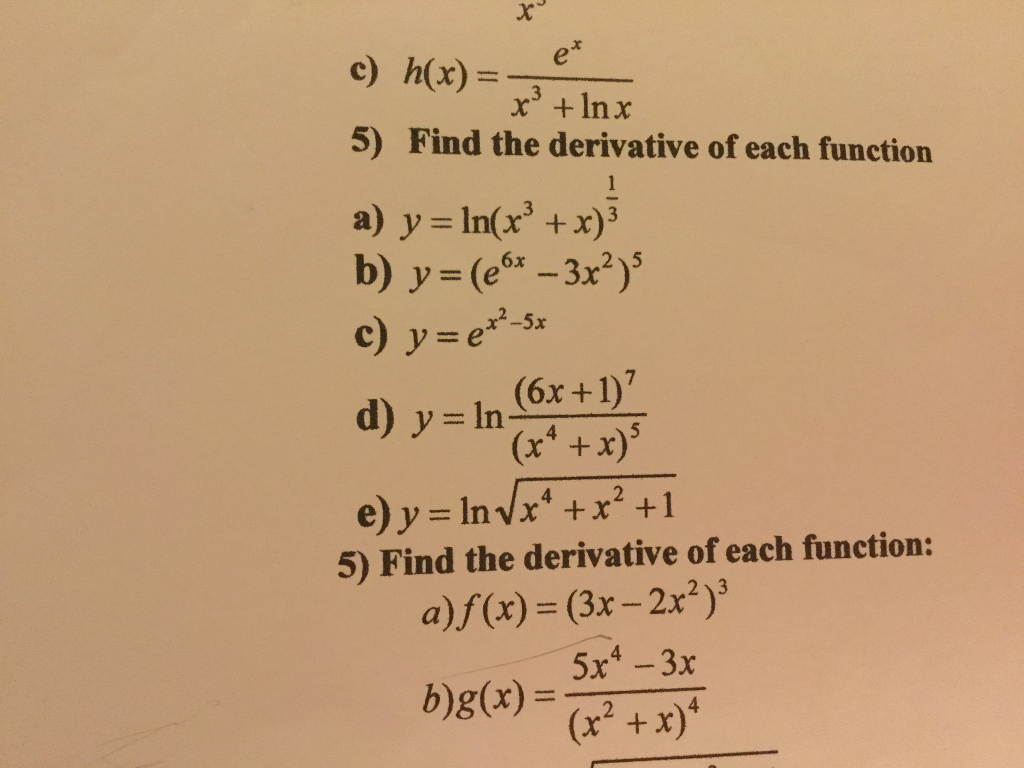



Find The Derivative Of Each Function Y Ln X 3 Chegg Com
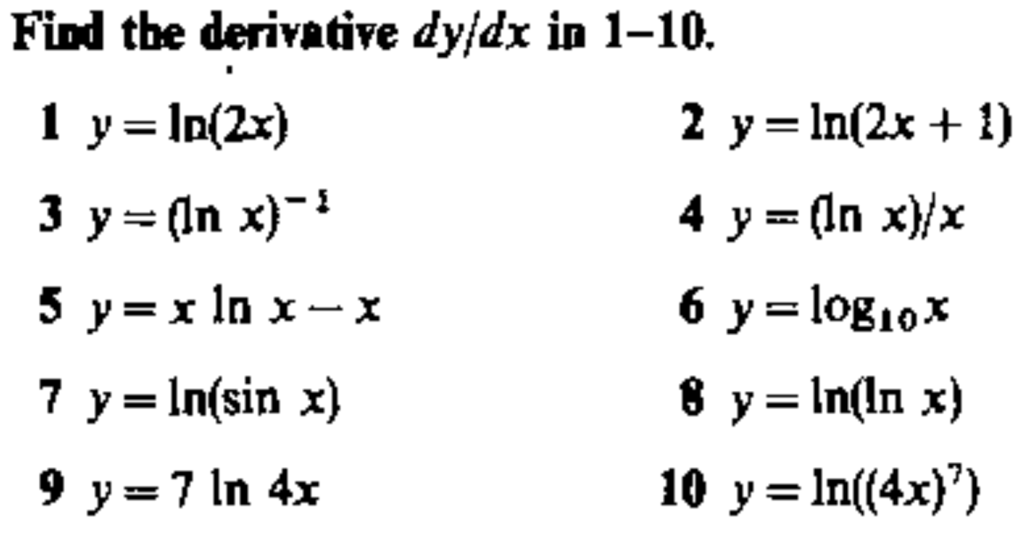



Find The Derivative Dyjdx In 1 10 1 Y Ln 2 X 3 Chegg Com
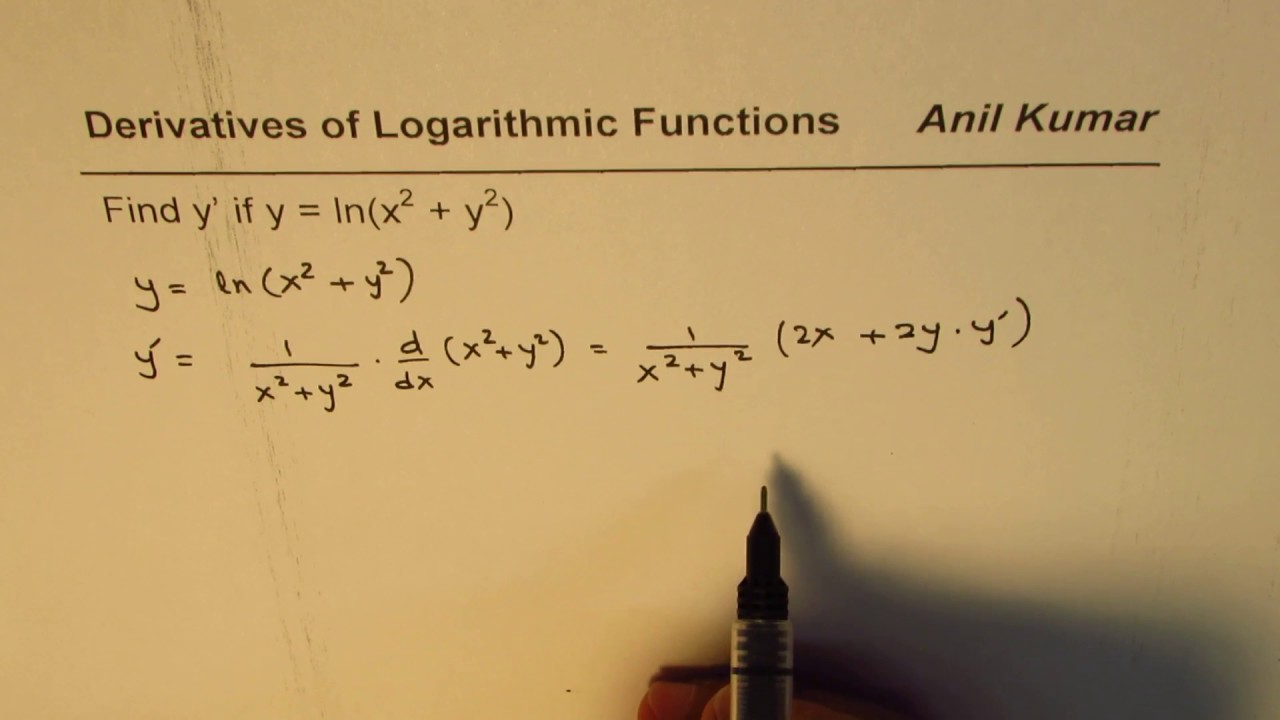



Implicit Derivation Of Logarithmic Function Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube



7 1 The Natural Logarithm Function
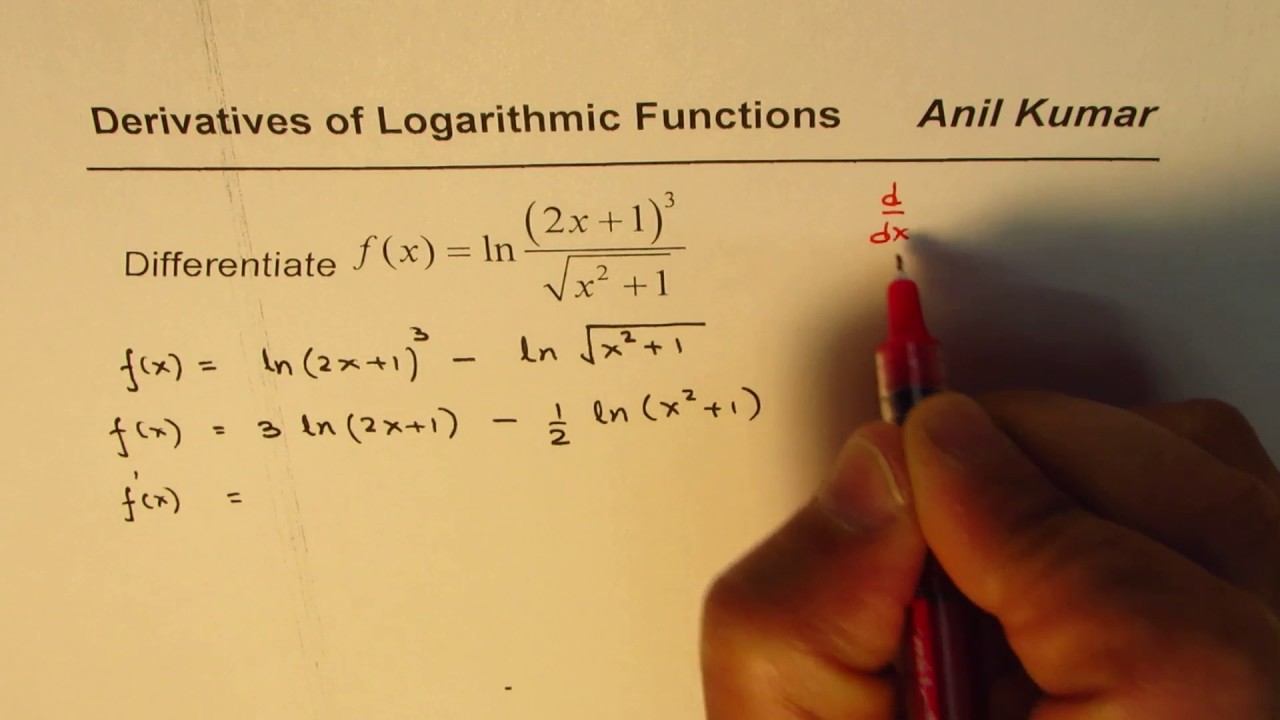



Calculus Natural Log Derivatives Ln 2x 1 3 Sqrt X 2 1 Youtube




Partial Differentiation And Multiple Integrals Pdf Free Download
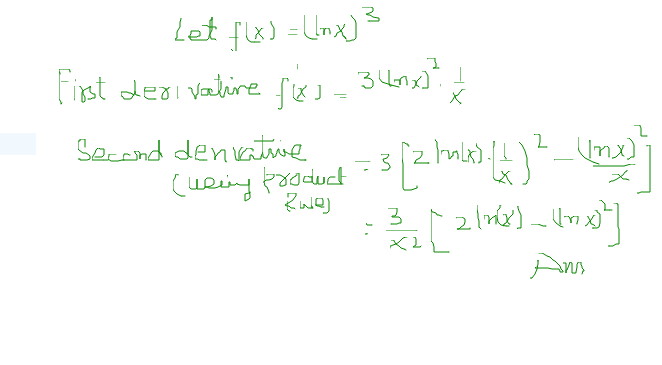



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Lnx 3 Socratic




Calculate The Directional Derivative Of Chegg Com




Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
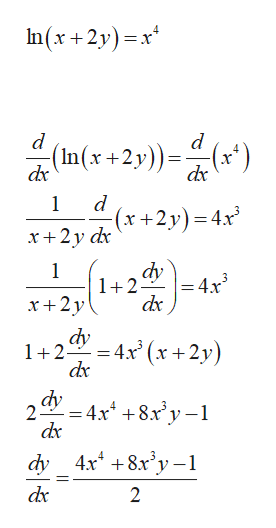



Answered Suppose Ln X 2y X4 Use Implicit Bartleby
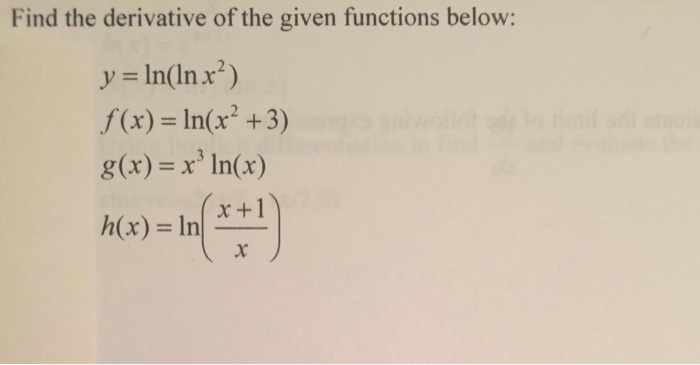



Find The Derivative Of The Given Functions Below Y Chegg Com




Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 3 Compute The Partial Derivatives Of The First And Second Order Mathematics Stack Exchange




Differentiate Y Ln X 3 Youtube




Find 1st And 2nd Derivatives For Y Ln X 2 5x Youtube




What Is The Equation Of The Tangent Line Of F X Ln X 3 X 7x At X 3 Socratic



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




1 Point Let Y Ln X2 Y2 Determine The Derivative Gauthmath




How To Find Dy Dx When Ln Xy X Y Quora




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps
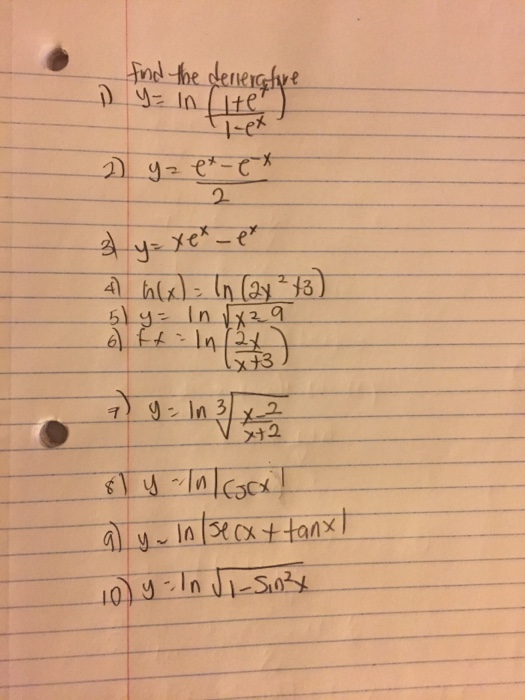



Find The Derivative Y Ln 1 E 1 Ex Y E X Chegg Com




Second Derivative Of Ln X Sqrt 1 X 2 Youtube




Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Ln 4 Chegg Com




Derivatives Days Ppt Download
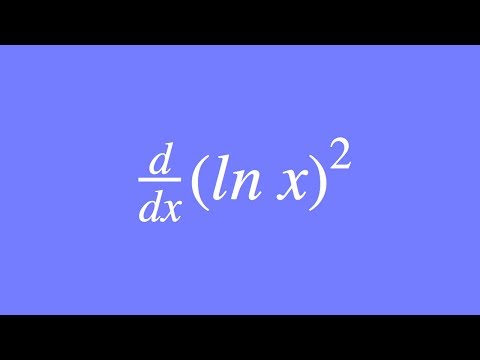



How To Differentiate Ln X 2 Using The Chain Rule Youtube
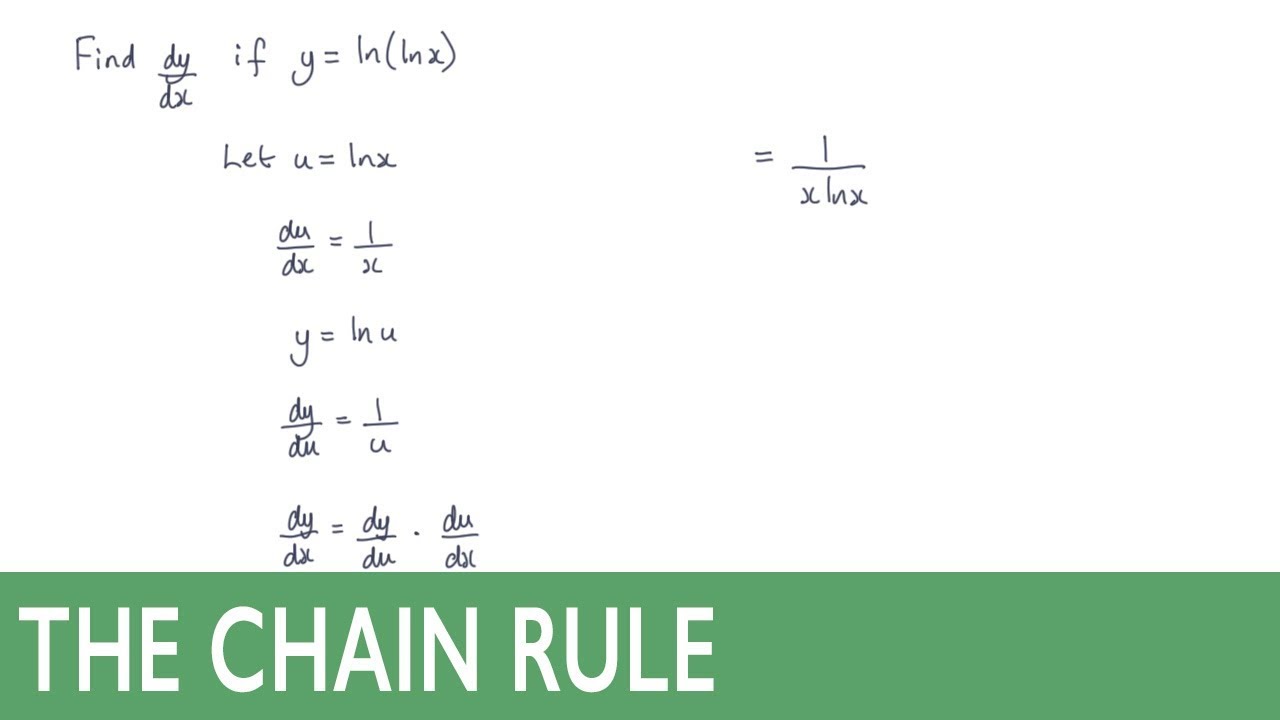



How To Differentiate Y Ln Lnx Using The Chain Rule Youtube
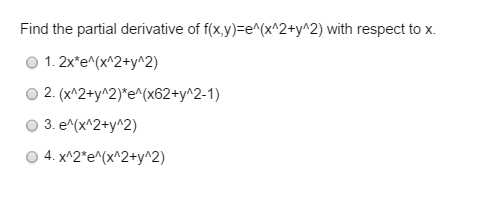



Find The Partial Derivative Of F X Y E X2 Y2 With Chegg Com



What Is The Differentiation Of Ln X And Log X Quora
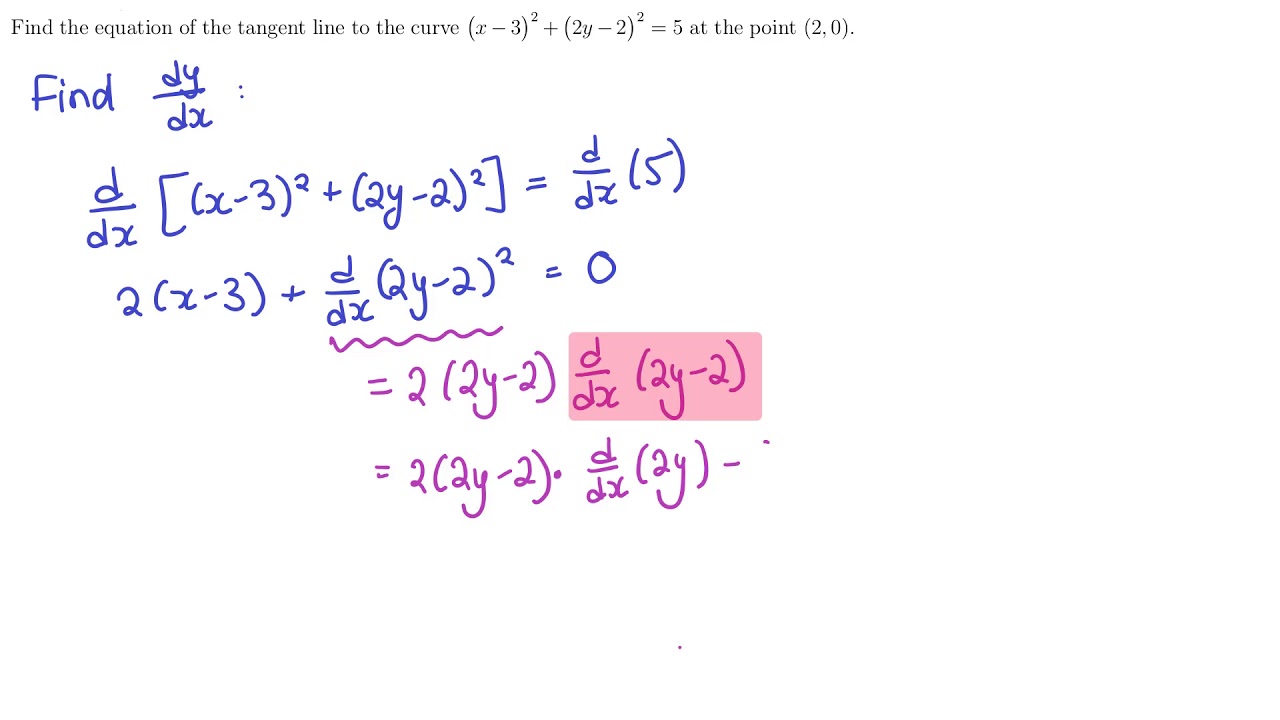



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation
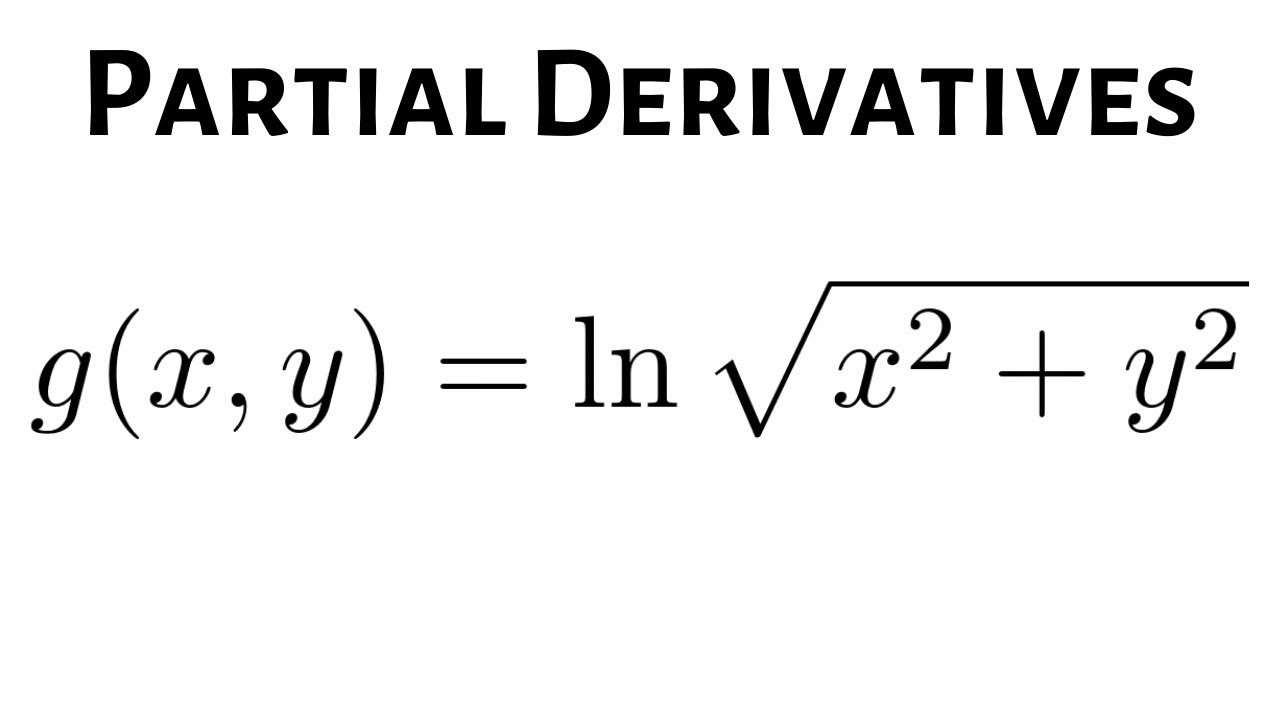



Larson Calculus 13 3 28 First Partial Derivatives Of G X Y Ln Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Youtube
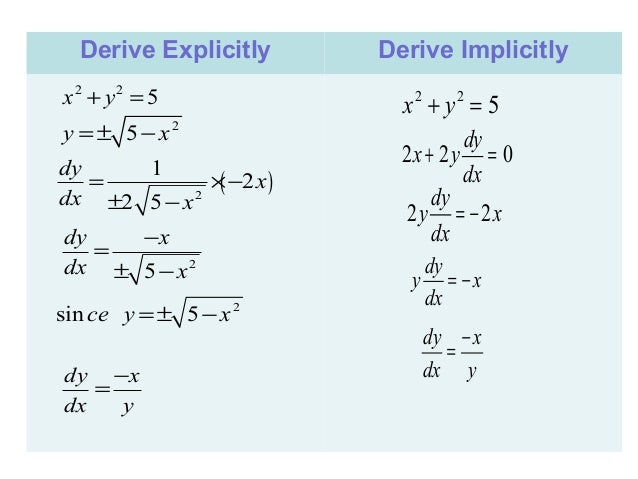



4 2 Derivatives Of Logarithmic Functions




Find Y For Ln X Y Arctan Xy Mathematics Stack Exchange



How Do You Determine Whether The Function F X Ln X 2 7 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down And Its Intervals Socratic



1
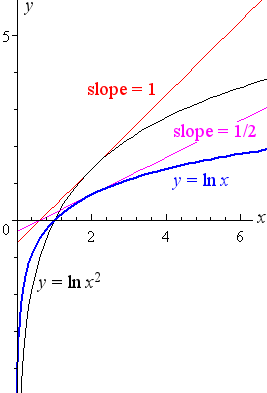



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Differentiation Ii Exam Questions Pdf




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿